Jul 10, 2025
How AI in Recruiting is Revolutionizing Medicine and Healthcare
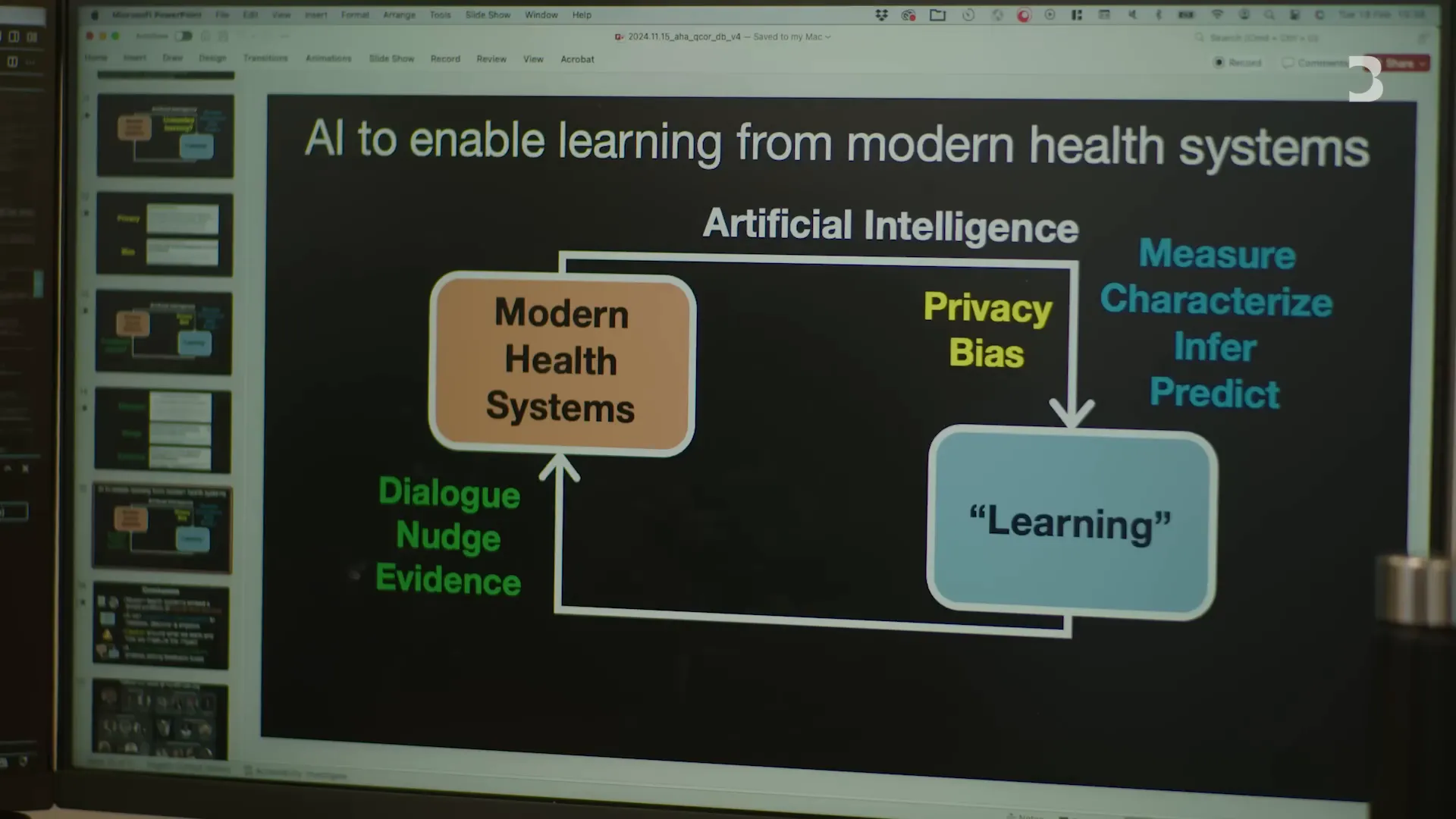
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept limited to science fiction. It has become a foundational change in many fields, especially in health care, where it is transforming how we diagnose, treat, and manage diseases. Dr. Rohan Khera, a cardiologist and data scientist at Yale Medicine, is at the forefront of this revolution, harnessing AI to detect cardiovascular abnormalities invisible to the naked eye. This article explores the profound impact of AI in medicine, with a special focus on how AI in recruiting talent and technology is shaping the future of healthcare delivery and innovation.
Understanding AI as a Foundational Shift in Healthcare
When discussing AI in healthcare, it is essential to recognize it as a transformative toolset, much like algebra was for mathematics. This analogy highlights the depth of change AI brings, fundamentally altering how medical professionals approach diagnostic testing and patient care.
Traditionally, interpreting diagnostic tests required significant expertise, often limiting access to timely and accurate diagnoses. AI is changing that by allowing for more effective interpretation of these tests without necessitating the same level of specialized knowledge. This shift is enabling new patterns of care to emerge, where AI augments human capabilities rather than replacing them.
The Expanding Role of AI in Medicine
AI has been part of healthcare for decades, but its mainstream recognition has accelerated recently, especially with the rise of generative AI models like ChatGPT. Initially, AI applications in healthcare focused on tasks such as transcribing doctors’ notes or enhancing patient interactions through chatbots.
However, generative AI is now supercharging capabilities in multiple critical areas:
- Predicting future health risks
- Making faster and more accurate diagnoses
- Accelerating drug discovery for novel treatments
These advances are not theoretical—they have been rapidly developing over the past five years as AI models have become more adept at working with complex healthcare data.
For example, AI can identify individualized signatures that predict how a patient might respond to a specific treatment or therapy, enabling more personalized and effective care. This capability represents a significant leap from the “one size fits all” approach historically common in medicine.
Addressing Concerns and Risks of AI in Healthcare
Despite the excitement around AI, both clinicians and patients have valid concerns about how these technologies will be integrated into healthcare workflows. Common questions include:
- How will AI be used to inform medical decisions?
- What are the risks of errors such as false positives or false negatives?
- Who will be responsible for AI-driven decisions?
These concerns have spurred the involvement of regulatory and professional organizations to ensure AI is used responsibly. For example, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees certain AI applications in healthcare, while groups like the American Medical Association (AMA) and the National Academy of Medicine provide guidelines and codes of conduct for ethical AI use.
Such oversight is critical to balancing innovation with patient safety and trust. Clinicians, too, play a vital role by interpreting AI outputs in the context of patient preferences and clinical judgment. AI tools are designed to assist—not replace—human expertise.
AI in Recruiting and Innovation: The Role of Academia and Industry
While large AI labs such as Google and OpenAI aim to disrupt healthcare broadly, specialized academic labs focus on applying AI to particular medical fields. One such example is Yale’s Cardiovascular Data Science Lab (CARS Lab), founded by Dr. Khera in 2020.
Academic institutions often have different priorities than startups. They emphasize fine-tuning AI models, developing ethical frameworks, and ensuring equitable access to technology. This contrasts with venture capital-funded startups, which have seen substantial investment—around $11 billion in 2024 alone—aimed at rapidly bringing AI solutions to market.

This dynamic ecosystem of academia and industry drives both innovation and responsible deployment of AI in healthcare. The collaboration ensures that AI tools meet rigorous standards before reaching patients.
The Cardiovascular Data Science Lab: A Case Study in AI Innovation
The CARS Lab at Yale Medicine exemplifies how AI can revolutionize specialty care. Their work spans diagnostics, precision medicine, and cardiac imaging, focusing on improving patient outcomes through AI-driven insights.
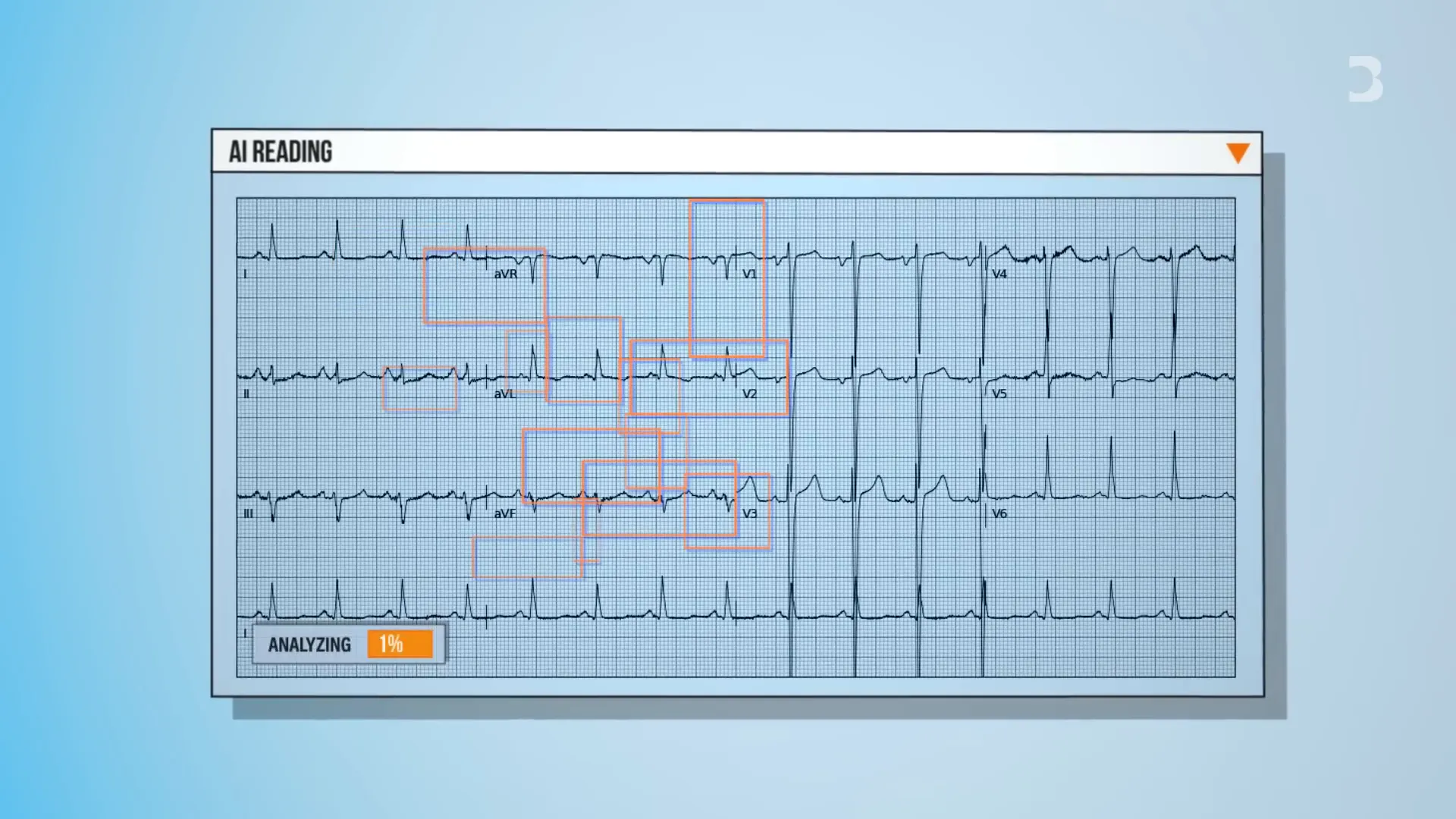
A standout project is the ECG GPT, a generative AI tool that interprets electrocardiograms (ECGs)—electrical recordings of the heart—by generating detailed reports.
Traditionally, a cardiologist would need to analyze ECGs, but ECG GPT can provide accurate readings accessible worldwide. This democratizes diagnostic capabilities, especially in regions lacking specialist cardiologists.
For example, the AI can detect subtle signals in specific ECG leads indicating left ventricular systolic dysfunction, a condition associated with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. This kind of detection surpasses human visual interpretation, highlighting AI’s potential to uncover hidden clinical information.
Importantly, the lab focuses on developing app-based solutions rather than complex integrations into large health systems, aiming to make these tools broadly accessible.
Challenges and the Path Forward for AI in Healthcare
Despite rapid progress, many challenges remain before AI becomes a standard part of clinical practice. Regulatory frameworks must adapt to oversee AI tools effectively, ensuring they are safe, fair, and equitable.
Concerns about AI-driven misdiagnoses currently appear limited because human doctors remain involved in final decisions. However, robust validation and continuous monitoring are essential to maintain trust and safety.
Ultimately, the question is not just whether AI will make us healthier, but how we ensure equitable access and proper use of these technologies. The benefits of AI systems depend on our collective willingness and ability to use them responsibly.
The Broader Impact of AI: A Transformational Innovation
Reflecting on the transformative innovations of our time, Dr. Khera points to foundational technologies like the transistor, the camera, the telephone, and the World Wide Web as enablers of modern healthcare advancements such as telemedicine, electronic health records, and MRI imaging.
AI belongs in this category of game-changing technologies. It is poised to revolutionize not just how we diagnose and treat disease but also how we recruit talent and develop new healthcare solutions.
In fact, AI in recruiting plays a critical role in healthcare innovation by identifying the right experts, data scientists, and clinicians to develop and deploy AI tools effectively. This ensures that AI initiatives are driven by diverse, skilled teams committed to ethical and impactful outcomes.
Conclusion: Embracing AI in Recruiting and Medicine for a Healthier Future
The integration of AI in healthcare is a foundational shift comparable to the advent of algebra in mathematics. From improving diagnostic testing to enabling personalized treatments, AI is transforming medicine at an unprecedented pace.
Yet, this transformation requires careful oversight, collaboration between academia and industry, and a commitment to responsible use. AI in recruiting helps build the expert teams necessary to navigate this complex landscape.
As AI continues to evolve, it promises to expand access, improve accuracy, and accelerate innovation in medicine. By embracing AI thoughtfully and ethically, we can unlock its full potential to save lives and enhance health worldwide.
AI is not just the future of healthcare—it is already reshaping the present, driving us toward a more precise, accessible, and equitable medical system.